
One of our main priorities is to ensure universal access to, and informed use of effective contraception. Millions of people lack the knowledge and information to determine when or whether they have children, and they are unable to protect themselves against sexually transmitted infections (STIs).
Articles about Contraception
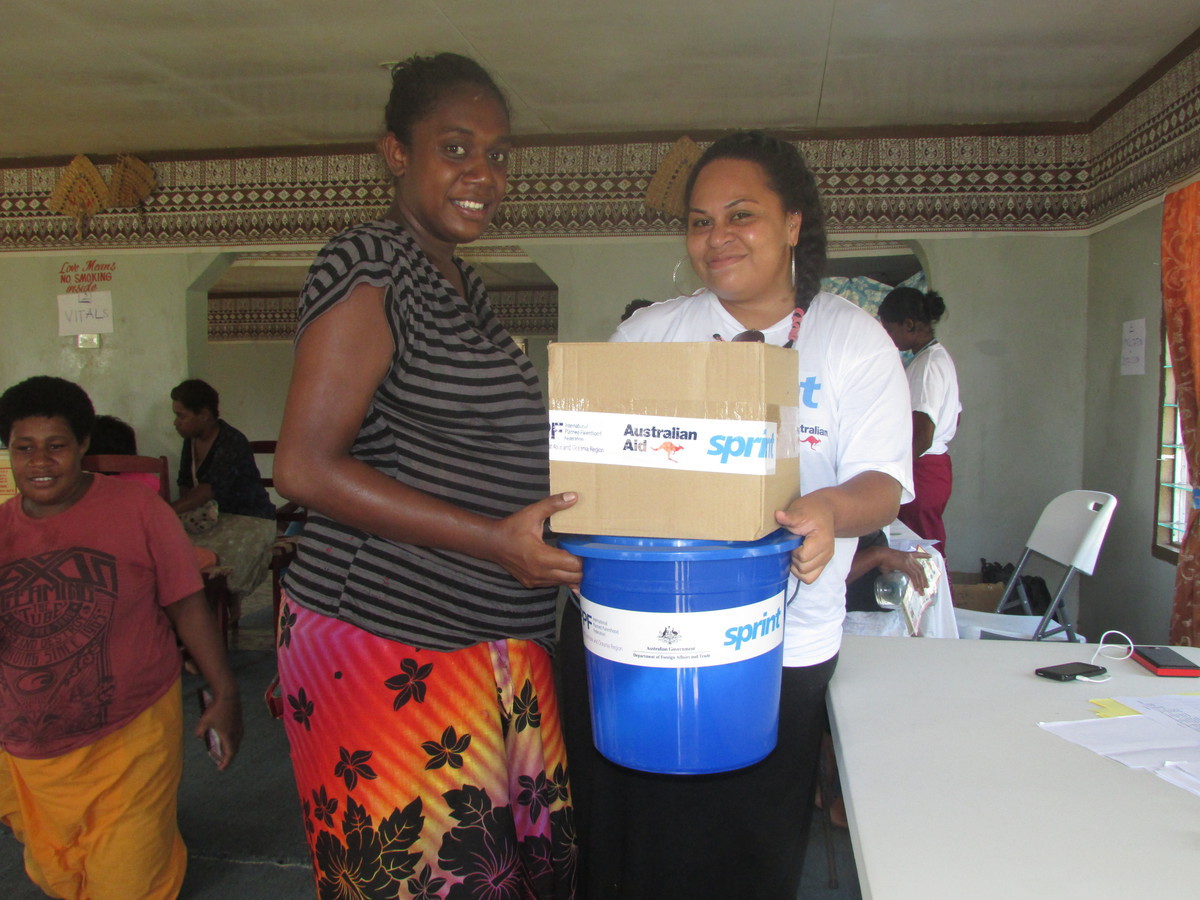

Fiji update
One month on the Cyclone Winston hit Fiji, IPPF-SPRINT is still providing sexual, reproductive and maternal care to cyclone-affected population.
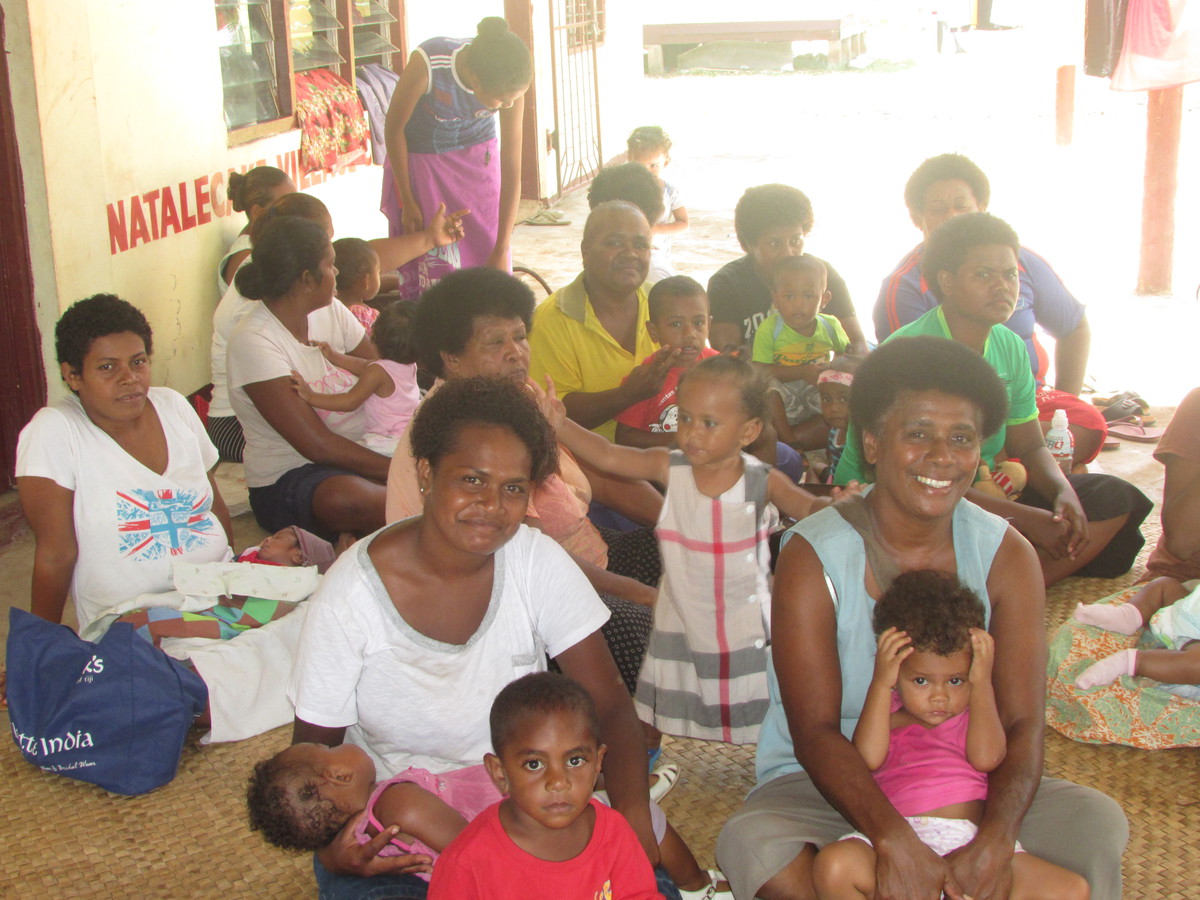

Emergency update from Fiji
One month on from Cyclone Winston, IPPF has helped hundreds of families, including new mothers and pregnant women. Thousands of people are disaplaced and 43 have now been confirmed dead in the worst tropical super-storm to have ever hit the Pacific. IPPF’s humanitarian wing, the SPRINT Initiative, is solely funded by the Australian Government to provide life-saving sexual and reproductive health services following a humanitarian crisis. The Australian Government provided an additional AUD $100,000 to ensure SPRINT could respond to the worst affected populations. IPPF’s assistance includes distributing hygiene and dignity kits to pregnant women and new mothers, providing maternal and neonatal healthcare, providing family planning and prevention programs to reduce the spread of sexually transmitted infections, including HIV. There has been an urgent need to respond to the immediate sexual and reproductive health needs of communities, specifically vulnerable groups such as pregnant and lactating women and women & girls at risk of gender-based violence. In crisis settings rates of gender-based violence drastically increase, and SPRINT has provided survivors with emergency care and services. IPPF-SPRINT has reproductive health missions in the provinces of Nataleira, Natalecake, Vadravadra. The Ministry of Health, under the Fiji Government, has also committed their medical staff to IPPF's medical camps. A key partner to the humanitarian repsonse is IPPF's local member association, the Reproductive and Family Health Association of Fiji (RFHAF). The Australian Minister for Foreign Affairs, the Honourable Julie Bishop paid a visit to IPPF-SPRINT’s SRH mission in early March to observe the work of the Australian-funded response. The Minister also distributed hygiene kits to the affected population in Rakiraki hospital in western Fiji. Apart from providing key sexual reproductive services, IPPF-SPRINT is also providing basic medical assistance to those affected.
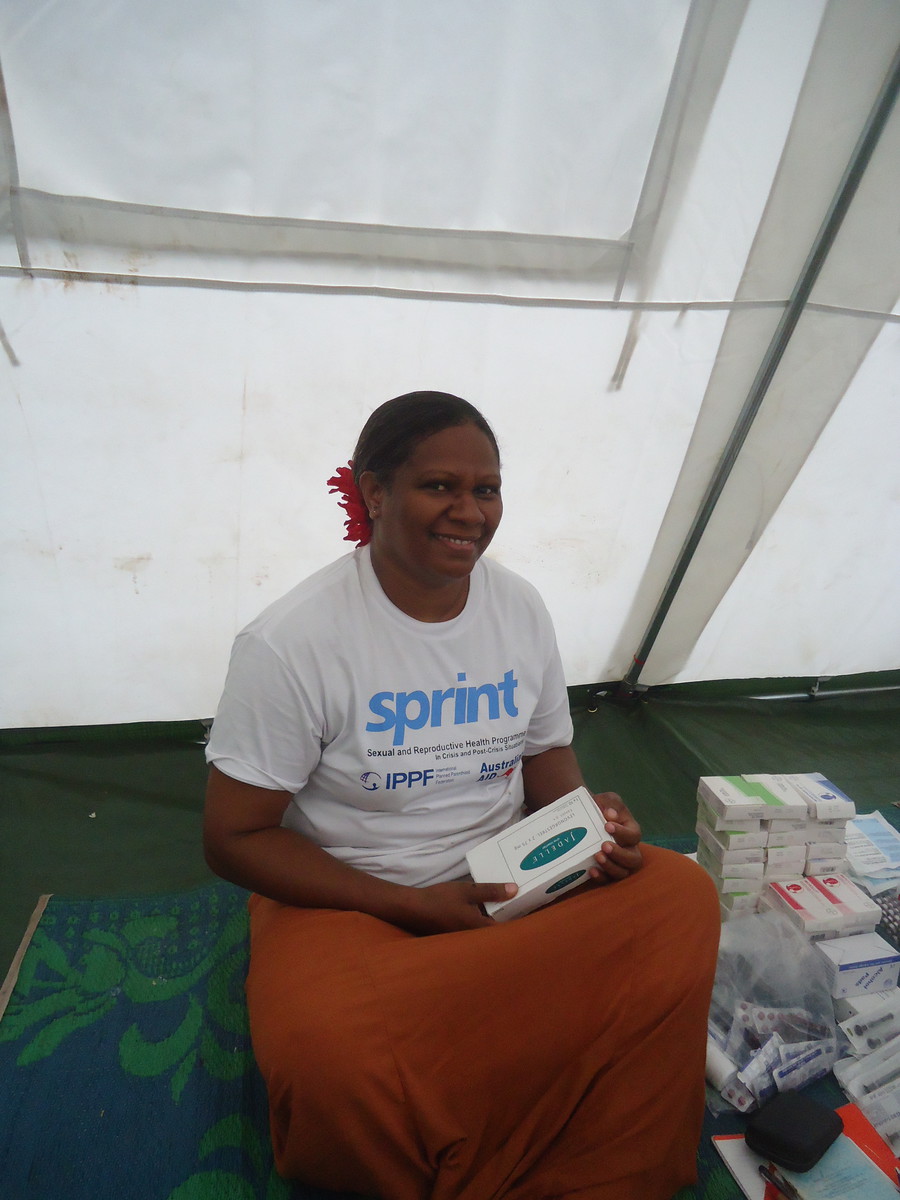

Overcoming barriers to family planning in Vanuatu: Julie's experience at IPPF-SPRINT
Julie was a midwife with the Ministry of Health for 20 years before she joined the Vanuatu Family Health Association (VFHA) as nurse and project manager for IPPF's SPRINT Initiative response in Vanuatu. When Cyclone Pam hit Vanuatu, the SPRINT Initiative and VHFA started providing life-saving services to the Island, Tanna, which was the population worst affected by the typhoon. Many communities there live remotely, in grass huts, with no immediate access to medical care. Julie was there with the VFHA team. “When I first came here we used the kitchen to operate from. On my second trip, we created a clinic in our youth centre, and used the nearby health post for clinical procedures. Soon we saw more patients pouring in, which created a huge demand for space." Health conditions are very low. Even before the cyclone hit the island, it was reported that the average mother loses two pregnancies each, in her lifetime. Every person in the village knows at least one mother who has died during child birth. Access and knowledge to family planning is overlooked as traditional practices are used first. As Julie explains, advocating about family planning is a challenge in the area, also for language barriers. “Talking about birth-spacing and talking in the regional dialect of Tanna is a problem. Most of us in Vanuatu speak Bislama, but people here in Tanna aren’t well versed with it. However, we try our level best with all possible methods including sign language and demos to impart knowledge about family planning.” Family planning services are just a part of the IPPF-SPRINT Cyclone Pam response, that also included general health check-up, counselling and awareness about Sexual and Gender Based Violence, maternal care and awareness and prevention of HIV and Sexually Transmitted Infections (STI).

IPPF welcomes new UN commentary on indivisible right to sexual and reproductive health
On International Women’s Day, the International Planned Parenthood Federation (IPPF) has welcomed a new commentary from UN experts which says that the right to sexual and reproductive health is indivisible from other human rights. “It is absolutely right for the Committee to address the issue of sexual and reproductive health specifically, today of all days,” said Tewodros Melesse, IPPF’s Director General. “Sadly millions of women are still denied their basic rights because they are poor, because they suffer discrimination or because they lack legal protection.” The 18 independent members of the Committee on Economic, Social and Cultural Rights said that the right to sexual and reproductive health was not only an integral part of the general right to health, but fundamentally linked to the enjoyment of many other human rights, including the rights to education, work and equality. They said that a lack of care for mothers in childbirth or a lack of access to safe abortion, often leading to maternal death, constitutes a violation of the right to life, and in certain circumstances can amount to torture. “No woman should die in childbirth in 2016 because of a lack of adequate care,” said Mr Melesse. “We know that access to safe abortion saves women’s lives, yet millions are denied that right.” IPPF is a network of sexual and reproductive health and rights organisations in 170 countries that are equipped to monitor and respond to any member of the public who wants information, services, contraception and access to abortion and are available to serve at the first point of response. For further information and interviews contact press office 02079398227
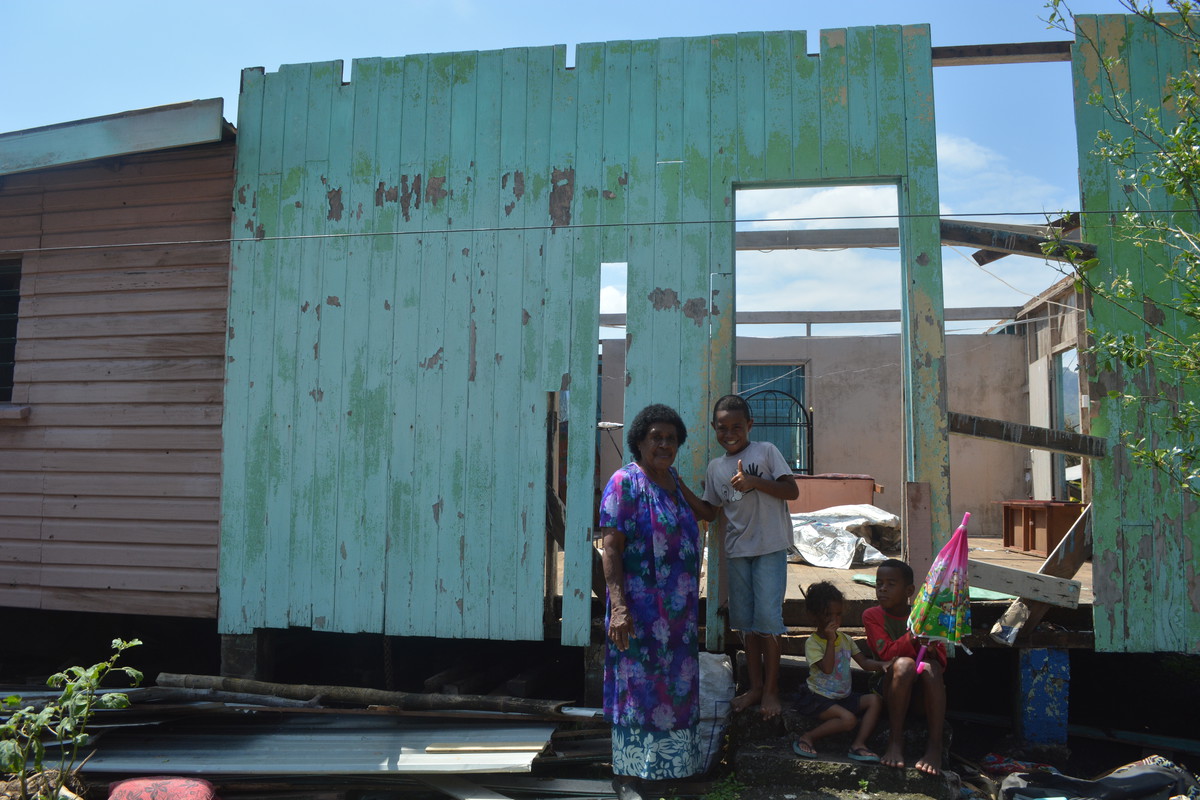

“I have never experienced such a strong cyclone in my 77 years of life.”
“I have never experienced such a strong cyclone in my 77 years of life.” Jokaveti Bavou lives in the village of Drauniivi, in the Fijian province of Ra. It was right in the path of Cyclone Winston, the strongest storm to ever strike the Southern Hemisphere. A week on from the disaster, Jokaveti, her son Jim and her grandchildren are safe. But there is no longer a roof on her house, and precious little left inside. In a village of 910 people, 75 houses were completed destroyed and about 65 damaged. Jokaveti was in her house with her grandchildren when Cyclone Winston arrived. “On Saturday night the winds started to increase. I told Jim that I was not sure of the house; I didn’t believe that it would be able to keep us safe. I told him that if the house started to collapse, we would run to his house for safety.” “The wind was getting stronger and when I looked at the back door, it had blown open. I took a hammer and nail to it. But when I got back to the other room, the main door had blown open and the wind was really strong. Then the wind took the roof off my house.” “I told my granddaughter that everything was terrifying and we needed to go and hide somewhere. It was not safe to be in the house because of the flying debris.” “I got out and my son called out from his house and told us that we should go and hide underneath our house. He tried to come out of his house to save us, but the wind was so strong and roofing iron was flying around.” “I went underneath my house with my grandchildren holding a lamp and stayed there until the wind died. My son’s eyes never left us. Luckily for us a corrugated roofing iron flew and covered where we were hiding. I just cried and continued to thank God for keeping us safe.” “I could sense fear from all of us including my grandchildren. They were crying too. My son kept on calling to check on us until the wind died down.” Miraculously, no-one from Jokaveti’s family or the village was killed or seriously injured. IPPF is establishing centers in the Northern and Western parts of Fiji to provide medical services, especially those that deal with maternal and child health and sexual and reproductive health. It is working closely with the Reproductive and Family Health Association of Fiji (IPPF’s member in Fiji), UNFPA Pacific, Empower Pacific, Fiji’s Ministry of Health and Medical Services. Donate now!

IPPF calls for G7 leaders to prioritize the full range of sexual and reproductive health care services in Universal Health Coverage
18 February, Tokyo:The International Planned Parenthood Federation (IPPF) calls for G7 leaders to prioritize the full range of sexual and reproductive health care services in plans for Universal Health Coverage in their forthcoming Ise Shima G7 Summit in May. IPPF made this call at this week’s G7 Health Experts’ Meeting in Tokyo. IPPF said sexual and reproductive health care (SRH)services are essential because they save lives, are cost effective and offer universal benefits. IPPF highlighted that SRH services are critical to achieving women’s empowerment, equality and full participation in society. These services play a crucial part in the development of resilient health systems that can help reduce the impact of humanitarian disasters. Giselle Carino, IPPF Western Hemisphere Regional Director Designate, who attended at the meeting said: "Governments (public sector) cannot work alone to ensure that no-one is left behind. Locally-owned organizations, such as IPPF Member Associations, are working at the frontline supporting communities, particularly poor and underserved people including women and adolescents, to make a real and sustainable difference in their health status and realize human security. G7 leaders must recognize the role of civil society in health system strengthening and building a new global health architecture". IPPF also calls for: The principle of Universal Health Coverage: that everyone has the right to health without facing financial hardship and no social groups can be left behind. Essential sexual, reproductive, maternal, new-born, child and adolescent health services at the primary care level should be a priority of Universal Health Coverage because investment in these services is among the most cost-effective interventions that a health system can provide. The importance of the social and gender determinants of health should be recognized by mainstreaming gender equality into Universal Health Coverage and national health strategies. Making significant progress on both targets 3.7 and 3.8 would be transformative. Therefore IPPF urges the G7 to prioritize discussion of how these targets can be achieved during preparations for the Ise-Shima summit and in particular calls on the G7 to ensure that sexual and reproductive health services are prioritized in plans for Universal Health Coverage.
Evidence Project
Under the Evidence project, IPPF is undertaking innovative research on respecting, protecting and promoting human rights in family planning/reproductive health services and ensuring community voices are part of efforts to improve and strengthen family planning programming. The Evidence Project uses implementation science to improve family planning policies, programs, and practices. Led by the Population Council in partnership with INDEPTH Network, International Planned Parenthood Federation, PATH, Population Reference Bureau, and the project’s University Resource Network, the five-year project (2013–2018) is investigating which strategies work best in improving, expanding, and sustaining family planning services. IPPF is leading on two cross-cutting areas of research. Firstly under the Evidence project, we are undertaking research on how the respect and protection of human rights of women and girls can be instituted and operationalised, and how programs can be held accountable for providing high-quality services. http://evidenceproject.popcouncil.org/technical-areas-and-activities/equity-rights-and-accountability. In order to address the need for indicators and tools for rights based family planning, the Evidence Project has partnered with global experts on human rights and family planning, the International Planned Parenthood Federation’s Sustainable Network Project (SIFPO/IPPF) and with colleagues at Reproductive Health Uganda (RHU) to develop and validate the Rights-Based Family Planning (RBFP) Service Delivery Index in Uganda. This is work is being undertaken in close collaboration with the Economic Policy Research Centre Uganda and University College London. In addition, we are undertaking a variety of activities that aim to contribute to a deeper knowledge of whether and how the implementation of accountability mechanisms in family planning and reproductive health programs improves clients’ access to and quality of services. For example, a multi-site case study in Uganda uses process evaluation methodology to explore the implementation of two social accountability programs, aiming to determine what hinders and facilitates engagement at the community level and its translation into improved social accountability processes and reproductive health outcomes. http://evidenceproject.popcouncil.org/accountability-mechanisms-to-improve-family-planning-and-reproductive-health-programs/

What does it take to save a life?
Imagine this: You’re pregnant, living at home, expecting to give birth in a few weeks’ time with the assistance of staff at your local clinic. But then disaster strikes. It could be a typhoon, or a tsunami or conflict. You flee and then find yourself in a makeshift camp where nothing is certain anymore. Bad enough you’ve left everything you own behind. Bad enough you no longer feel safe – you can’t lock a tent door. But you’re relying on people who you don’t know for food – and people you may not trust for security. And how will you give birth? When you hear of populations dislodged, yout think of the immediate challenges of food and shelter. But what about contraception and neo-natal services? What about the dangers of sexual violence that women and girls in particular face? This is why IPPF’s humanitarian arm SPRINT was founded: to ensure access to essential Sexual and Reproductive Health and Rights services for women, men and children in times of crisis. In Syria 46,500 women will suffer gender based violence, including rape, as a result of the ongoing conflict. This shows a great need to ensure that the human rights of women and girls are protected and able to access sexual and reproductive healthcare. The Syrian Family Planning Association is in the front line when it comes to dealing with domestic-based violence – the less-reported consequence of every war. The kind of violence facing one of our clients, Amal. Amal had bruises on her face and was in a fragile state when she was admitted to the Al-Halbouni Health clinic. She had been severely beaten by her husband. The SFPA is committed to involving men to find lasting solutions to issues of gender based violence. Thanks to the integrated package of support services provided by Al- Halbouni clinic to her and her husband, Amal now feels safer. “I feel more aware of my rights, and I know how to find help when I need it,” she said. Women and girls are disproportionately influenced by humanitarian crises exposed to early marriage, trafficking, rape, forced pregnancies, unattended service delivery during complicated pregnancies and delivery. The statistics are shocking: 26 million of the 100 million people are in need of humanitarian assistance, are women and adolescent girls of reproductive age 500 of these women and girls die every day from complications related to pregnancy and childbirths 85 % of those displaced by the 2010 floods were women and children More than 75% of Syrian refugees who fled are women and children Women and girls are 14 times more likely to die in disaster settings than men 7 out of 10 women are exposed to gender-based violence in crises situations unfolding right now. These deaths and violence are preventable. We could stop it by putting money and efforts into an integrated comprehensive package on reproductive health into the standard humanitarian response. Progress in targeting women and girls has been achieved in the past decade. But sexual and reproductive health services are often neglected in humanitarian emergencies and still remain a less universally acknowledged priority. Over the last 10 years, IPPF has reached millions of people during floods, conflicts, earthquakes, cyclones. When health care often collapsed, our Member Associations continued to serve the unreachable, which make three quarters of IPPF clients. All IPPF approaches are bottom-up, that means we build local capacity before, during and after crisis strikes – often engaging young people during humanitarian crisis as peer-peer educators and providers. The good news is the guidelines are developed. We know what needs to be done. What we need now is action from many different stakeholders.

Global response to Zika must provide contraceptives to all says IPPF
As a case of sexually transmitted Zika infection was reported in the US yesterday, the International Planned Parenthood Federation’s (IPPF) Director General, Tewodros Melesse urged that more must be done to ensure contraceptive access is at the forefront of the response. In a statement by IPPF’s Director General, Tewodros Melesse said in response to reports of Zika in Ireland and US yesterday. “The World Health Organization (WHO) on Monday declared Zika a Public Health Emergency of International Concern. Further guidelines are needed for a comprehensive effort to tackle the epidemic. We need more guidance from WHO to ensure that the rights of women are at the forefront of the Zika response. Updates are essential now that sexual transmission is emerging as a potential mode of infection that puts people at risk.” It is clear that further surveillance and research is necessary to confirm if this is a possible mode of transmission. If proved that the Zika virus can be sexually transmitted, it will be important to ensure the integration of sexually transmitted infections (STI) prevention strategies as part of control efforts. The Centres for Disease Control (CDC) reported that it is likely that the infection in the US was transmitted through sexual contact. IPPF will continue to monitor the situation. With this potential for sexual transmission, it is advised to ensure access to condoms and to promote use along with other forms of contraceptive methods. Male and female condoms are effective for preventing unintended pregnancies as well as the transmission of HIV and other sexually transmitted infections (STIs). In response to the calls for women to delay pregnancy in some of the affected countries, Mr Melesse said “It is essential to recognize that women have the right to make decisions about their reproduction, including if and when they have children, but this is not always possible in areas of poverty and where sexual and gender based violence rates are high.” “Delaying pregnancy will not be an option for some, so every response must be tailored to the individual. The Zika response must include a sensitive approach to pregnant women who are concerned and need testing, while access to contraception should be available to all. Governments must ensure that their medical services have the supplies for those whose want it. We recommend that strengthening family planning programs and access to safe abortion services for those women who need it and where it is permitted by law should be included in the strategies for responding to the Zika outbreak.” IPPF is a network of sexual and reproductive health and rights organisations in 170 countries that are equipped to monitor and respond to any member of the public who wants information, services, contraception and access to abortion and are available to serve at the first point of response. For further information and interviews contact press office 02079398227
Overcoming family planning challenges in Zambia
Every three months Felistus has to set off on a four hour walk across two mountains to get to her closest family planning services. Felistus’ husband, Peter, said: “Family planning helps us to enjoy our marriage without fear of unwanted pregnancies. Children grow healthier and we can have not have more than we can afford.” She has no alternative unless she wants to risk an unwanted pregnancy but the trips creates problems with her husband because the household tasks don’t get done and their five children are left unattended while she is away. In such remote locations the choice is a long walk to a service post or to use a Community Based Distributor (CBD) but there are some problems with the CBDs. They are not trained to administer long acting reversible contraceptives which means they are often only able to distribute condoms. One of the CBDs in Zambia, Kabungo, said: “When the people heard the Government is planning to introduce CBD to attend to their family planning needs they thought that all family planning methods would be available but since many CBDs are not trained to offer anything apart from condoms it is not possible to offer other methods. It discourages people because they expect the CBD to provide all family planning methods.” Prisca Simbeya, who’s a family planning champion in Zambia, said she thought it was time for the Government of Zambia to explore the underlying potential of the CBDs to reach out to the most underprivileged populations. She said they needed to build the capacity of the community based distributors so they could administer the injectable method of contraception which, she said, could be a good starting point for long last reversible methods of contraception. She added that they needed to cement the intervention to ensure that services were available as close to people as possible. Ms Simbeya said she thought that the Government also needed to be mindful of time since Zambia as a country made these commitments at the family planning summit in London three years ago. She said that if they didn’t act sooner rather than later it would be difficult to meet Zambia’s target which was a major factor in addressing high fertility rates.
Pagination
- Previous page
- Page 21
- Next page






